Hybrid Power Technologies, LLC
| Water-Cooled Reactors |
|
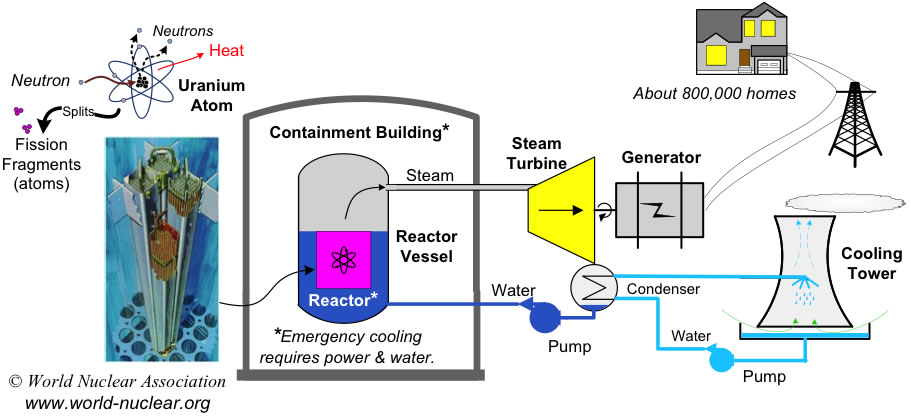
Modern nuclear reactors, while exceptionally safe, do have a few drawbacks: |
©2012, 2013 Hybrid Power Technologies, LLC
Last Modified: October 12, 2013
Hybrid Power Technologies, LLC |
||||||
| HOME HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE GAS-COOLED REACTORS WATER-COOLED REACTORS GAS TURBINES COMBINED CYCLE NEXT GENERATION ABOUT US CONTACT US | ||||||
©2012, 2013 Hybrid Power Technologies, LLC |
 |
|||||